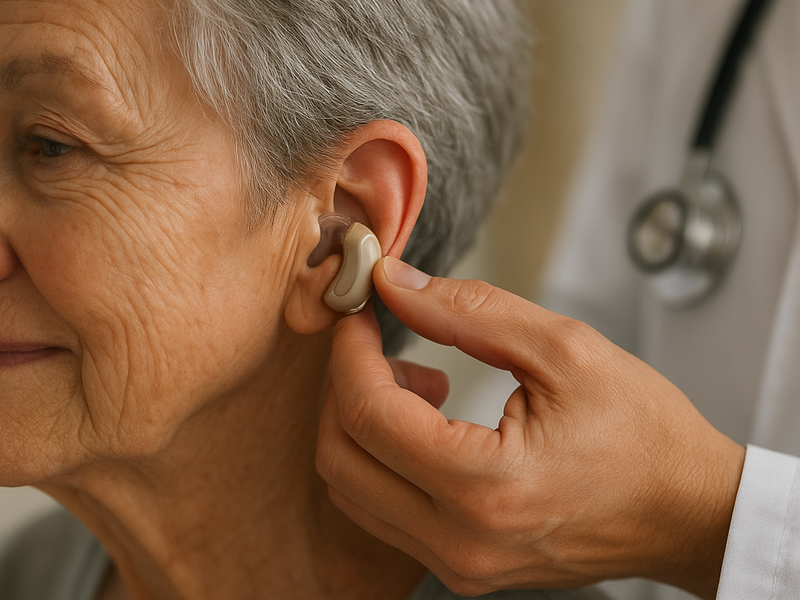
In ear hearing aids have transformed the way many people manage hearing loss by combining compact design with powerful digital processing. These devices sit inside the ear canal or in the outer ear, delivering sound directly where it is needed while keeping a low profile. For people seeking a discreet solution or a more natural listening experience, in ear options can be especially appealing. This article explores the landscape, what to look for, how to buy, and how to compare leading providers in the field.
What defines an in ear hearing aid and who might benefit In ear hearing aids come in several styles that share a common goal: deliver amplified sound from a small footprint that fits within the ear’s contours. The most common forms include completely in canal CIC devices that nest deep in the ear canal, in canal ITC devices that sit just inside the opening, and a broader category sometimes called in the ear devices that sit at the concha level but still remain far less conspicuous than traditional behind the ear models. The best choice depends on several factors including the degree of hearing loss, the shape and size of the ear canal, cosmetic preferences, and how the wearer uses the device during daily activities. People who value discretion, those with lifestyle demands that require a compact solution, and users who want minimal occlusion (the sensation of the ear being blocked) often gravitate toward in ear options. Modern in ear aids also emphasize ease of use, with intuitive controls and apps that let wearers adjust settings without needing frequent visits to a clinic.
Key features to consider When evaluating in ear devices, focus on technology that improves real world listening. Digital signal processing helps separate speech from background noise, while feedback suppression reduces whistling sounds. Multi microphone arrays can enhance directionality so conversations in noisy environments become more intelligible. Bluetooth or wireless streaming lets you hear phone calls, music, and video through the same device, which many users find transformative for daily routines. Rechargeability is another practical factor; many newer in ear aids offer rechargeable options, reducing the need for frequent battery changes. App compatibility is increasingly important as manufacturers provide smartphone interfaces for remote adjustments, battery status checks, and personalized programs. It is also worth considering tele-audiology support, which enables remote fine tuning and follow up without a visit to a clinic.
Design, fit, and real world use The physical fit of an in ear aid is highly personal. Some users prefer a completely custom shell that is molded to the ear, while others opt for a semi custom or standard size that can be adjusted by the ear canal’s anatomy. Maintenance matters too; in ear devices require careful cleaning and moisture protection, since the canal environment can be more challenging than behind the ear designs. Aesthetics should not be underestimated; a well designed product is not only about size but also about the ease of insertion, labeling of controls, and the clarity of the accompanying user interface. For many wearers, the ability to discreetly adjust volume or switch programs with simple taps or swipes on a connected app is a deciding factor.
How to buy: paths to ownership There are several legitimate paths to obtain in ear hearing aids, and the best choice depends on location, budget, and comfort with in-person visits. Traditional routes involve an audiology or hearing care professional who conducts a full hearing evaluation, verifies candidacy, and performs a precise fit. This route remains the gold standard for many because it ensures programming aligns with the wearer’s hearing profile. In some regions, ancillary clinics and hearing aid centers provide similar services with credentialing to ensure quality care.
In recent years, over the counter OTC options and online retailers have expanded access. OTC models are designed to be user friendly with self-fitting features and guided setup, suitable for mild to moderate hearing losses in many markets. Online retailers and teleaudiology services offer guidance, risk-free trials, and remote adjustments after purchase. Examples of online channels include brands that specialize in direct-to-consumer hearing care, as well as established clinics that offer remote fitting and ongoing support. Regardless of path, look for clear trial periods, transparent return policies, and access to remote adjustments or in-person follow ups if needed.
Comparing leading providers and platforms Top manufacturers often cited for in ear or near invisible devices include Phonak, Oticon, Signia, ReSound, Widex, and Starkey. All bring distinct design philosophies and feature sets to the market.
- Phonak emphasizes broad compatibility and strong speech understanding across environments. Its platforms commonly support robust wireless streaming and seamless integration with mobile devices, making it easy to switch between phone calls, music, and conversations.